
In its recently released 2015 Long-Term Reliability Assessment (2015 LTRA), the North American Electric Reliability Corporation (NERC) finds that the significant and accelerating transformation of the North American electric power system will require new approaches to system planning and operation to maintain adequate levels of reliability during the transition.
Key Details
The latest issuance of NERC’s annual 10-year assessment finds that ongoing retirements of fossil-fired and nuclear baseload capacity, combined with the growth in intermittent wind and solar resources, are directly impacting the behavior of the Bulk Power System (BPS) in ways that create new challenges for system planners and operators—and increased demand-side management and distributed energy resources have also introduced new challenges.
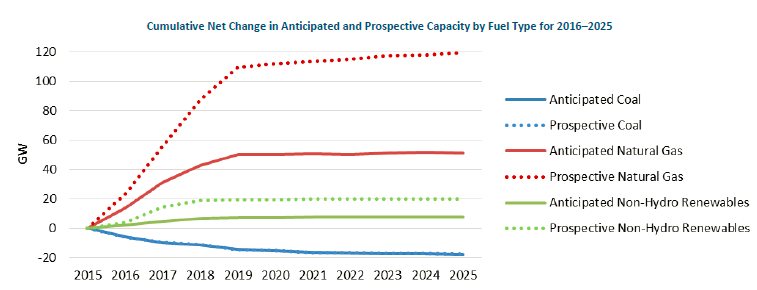
As the coal component of the generation fleet continues to decline, natural gas and renewable generation will continue to increase their roles in the future composition of the generation fleet. Natural gas capacity is projected to grow at an accelerated rate, adding 42 GW of anticipated generation capacity (10% of the total gas-fired capacity) by 2019. Renewable generation is projected to provide a larger contribution in the total capacity, increasing from 33 GW in 2015 to 40 GW by 2025.

Source: North American Electric Reliability Corp.
One challenge is that new generation resources will need to include sufficient voltage control, frequency support, and ramping capability in order to maintain the reliability of the BPS. NERC refers to these as “essential reliability services,” and the report includes a recommendation to policy makers to consider new measures to maintain reliability through this transition.
Further, the increased reliance on natural gas-fired generation continues to raise reliability concerns, and NERC finds that there is a need to further enhance the planning and coordination among gas and electric infrastructure operators to consider fuel deliverability, availability, and responses to contingencies.
Implications
The challenges of integrating variable renewable resources are not new. The industry has been analyzing, planning, and preparing to address these challenges for many years. However, this is the first time that NERC has directly called on all federal, state, and local policy makers to consider the “essential reliability services” provided by the current and future composition of resources to ensure the reliability of the bulk power system. Additional guidance will be outlined in NERC’s upcoming “Essential Reliability Services Taskforce Framework Report” in early 2016. While the degree of impact varies by region and rate of variable generation penetration, this suggests that the issue has outgrown that of a single utility’s footprint or a single balancing authority.
Substantial progress has already been made in addressing the interdependencies between the electric and gas industries. As natural gas-fired generation surpassed coal in 2015 as the predominant fuel source for generation (and natural gas is the leading fuel type for capacity additions), though, this issue continues to be a key source of concern for BPS reliability. The electric sector’s growing reliance on gas has increased the degree of interdependency of the two systems and the need for enhanced planning and coordination.
More Information
NERC: Reliability Assessments
This report is part of ScottMadden’s Fossil Minute series. To view all featured Fossil Minutes, please click here.
View More
Sussex Economic Advisors is now part of ScottMadden. We invite you to learn more about our expanded firm. Please use the Contact Us form to request additional information.